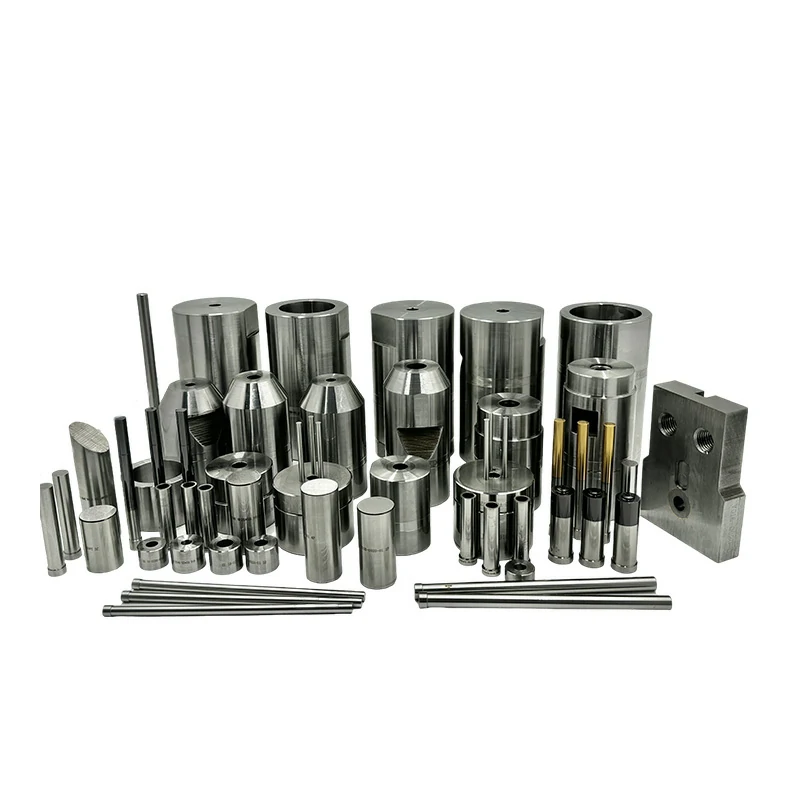
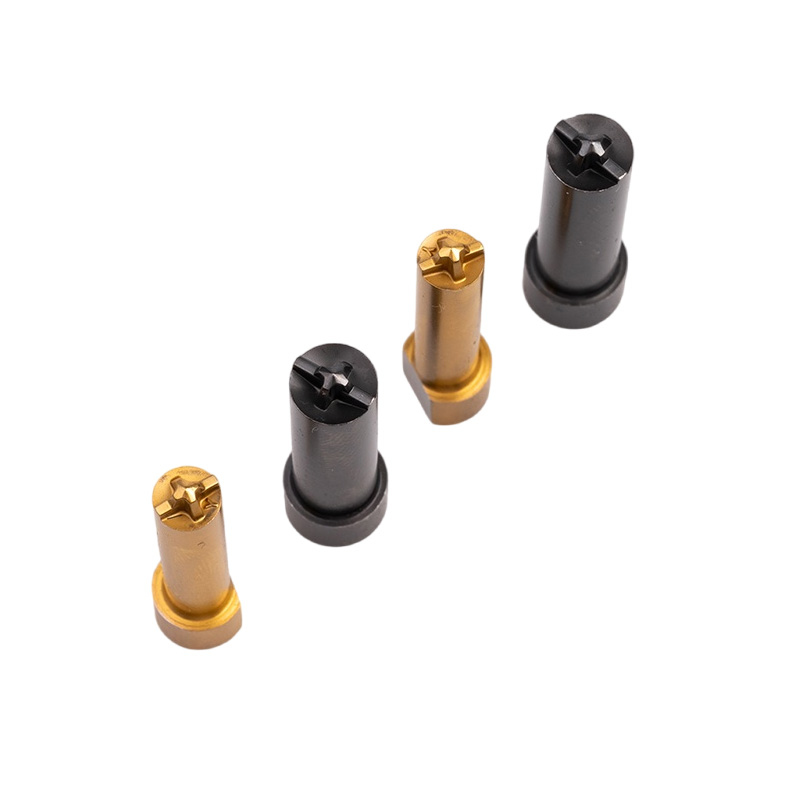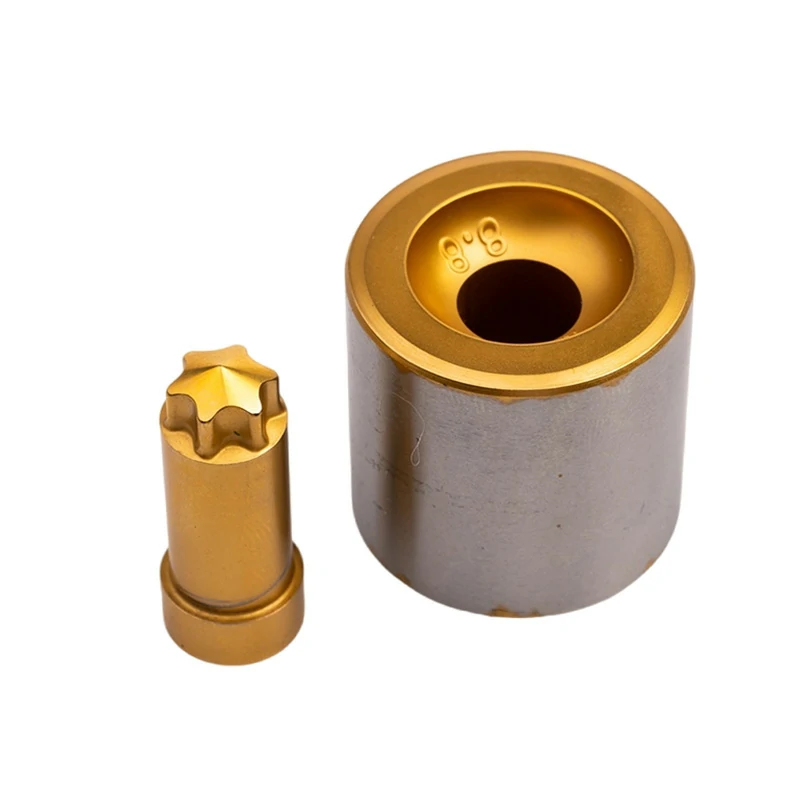
When it comes to high-speed, precision manufacturing of parts like bolts, screws, and rivets, you might have heard the term “cold heading die.” But what exactly does it mean? Understanding this tool is key to appreciating how mass production of these essential components happens efficiently.
A cold heading die is a specialized tool used to shape metal parts at room temperature. It enables the cold heading process, which is a fast, efficient way to produce bolts, screws, and other fasteners.
To fully understand its role, let’s explore what cold heading is, how it compares to cold forging, and why it’s so important in manufacturing.
Table of Contents
- What does “cold heading” mean?
- What is the difference between cold heading and cold forging?
- What is the cold headed manufacturing process?
- What is cold heading quality?
What does “cold heading” mean?
Cold heading is a manufacturing process that forms metal at room temperature using compressive force. It involves shaping wire or rods into specific forms without heating the material.
Cold heading means forming metal parts at room temperature using high pressure and dies. It produces strong and precise components without wasting material.
Dive Deeper: Why is Cold Heading Important?
Cold heading is vital because it combines speed, precision, and material efficiency. Unlike machining processes, cold heading eliminates scrap, making it cost-effective and environmentally friendly. It also enhances the material’s strength due to work hardening during the process.
Applications of Cold Heading
Cold heading is used to produce fasteners like:
- Bolts and screws
- Nuts and rivets
- Electrical contacts
What is the difference between cold heading and cold forging?
At first glance, cold heading and cold forging seem similar because both of them form metal parts at room temperature. However, there are key differences.
Cold heading focuses on forming metal part in less deformatin with wire or rod by a one die two blow machine such as screws and rivets, while cold forging involves shaping complex metal parts through multiple forming processes with a series of dies by a multi-station machine from 2 die 2 blow to 7 die 7 blow such as bolts with washers and nuts
Key Differences: Table Comparison
| Aspect | Cold Heading | Cold Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Carbon wire or Stainless wireDiameter from 2mm to 6mm | Carbon wire or Stainless wireDiameter from 6mm to 30mm |
| Process | Simple steps with a One Die Two Blow machine | Multiple steps with a Multi-station machine |
| Application | Small parts for fixing and connecting of furniture, construction, electronics, and appliances | Larger parts for fixing and fastening of larger parts applying in industries of automotive, machinery, aerospace and electric power |
Cold Heading or Cold Forging?
It depends on what products used in what industrial sectors.
What is the cold headed manufacturing process?
The cold heading process involves a series of precise steps to transform raw wire into finished parts. Here’s how it works:
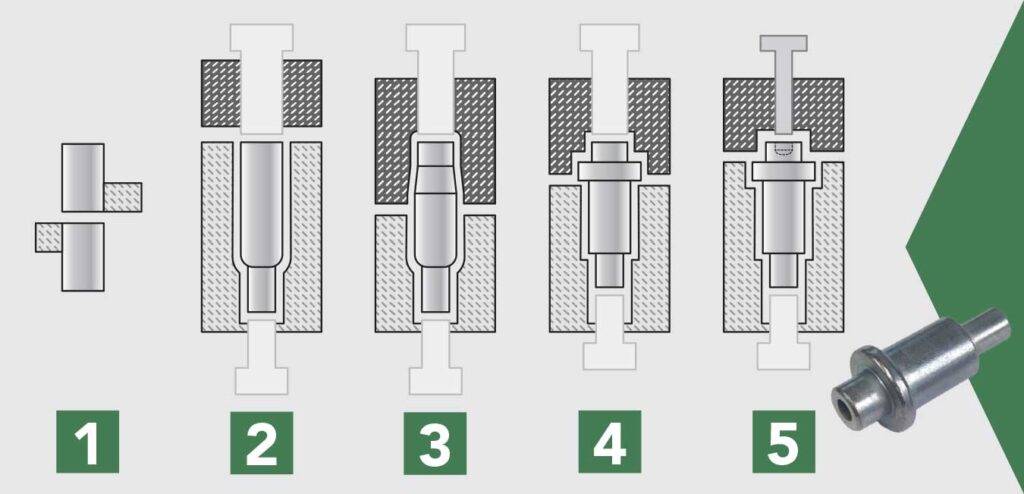
The cold heading process includes wire-cutting, wire-forming, head preliminary forming, head finally forming, and kicking out the finished parts using a heading machine set-up with a series of dies.
Steps in Cold Heading
- Wire Feeding: The wire is fed into the machine.
- Cutting: The wire is cut to the desired length.
- Forming: The wire piece is shaped using a die and punch.
- Trimming (optional): Excess material is removed for precision.
Advantages of Cold Headed Manufacturing
- High production speed
- Minimal material waste
- Improved part strength
- Lower production cost
What is cold heading quality?
Cold heading quality refers to the standards and precision achieved in the cold heading process. It ensures the manufactured parts meet exact specifications.
Cold heading quality involves strict control over dimensions, tolerances, and material integrity to produce reliable and high-performance parts.
Factors Affecting Cold Heading Quality
Several factors ensure cold heading quality, such as:
- Material Selection: Using high-quality wire ensures strength and precision.
- Die Design: Accurate dies create consistent results.
- Machine Calibration: Well-maintained machines guarantee dimensional accuracy.
- Inspection: Regular checks maintain quality control.
Quality Control Techniques
Manufacturers use tools like digital calipers, 3D scanners, and tensile testing to ensure quality. For critical parts, additional tests such as non-destructive testing (NDT) are performed.
Conclusion
Cold heading dies are essential tools in precision manufacturing. From bolts to rivets, they help create strong and accurate parts efficiently.





