In today’s manufacturing world, businesses constantly seek efficient, precise, and strong production methods. Cold heading stands out as a transformative metal-forming technique. Unlike traditional machining, which removes material, cold heading forms metal. This offers powerful economic, mechanical, and environmental advantages.
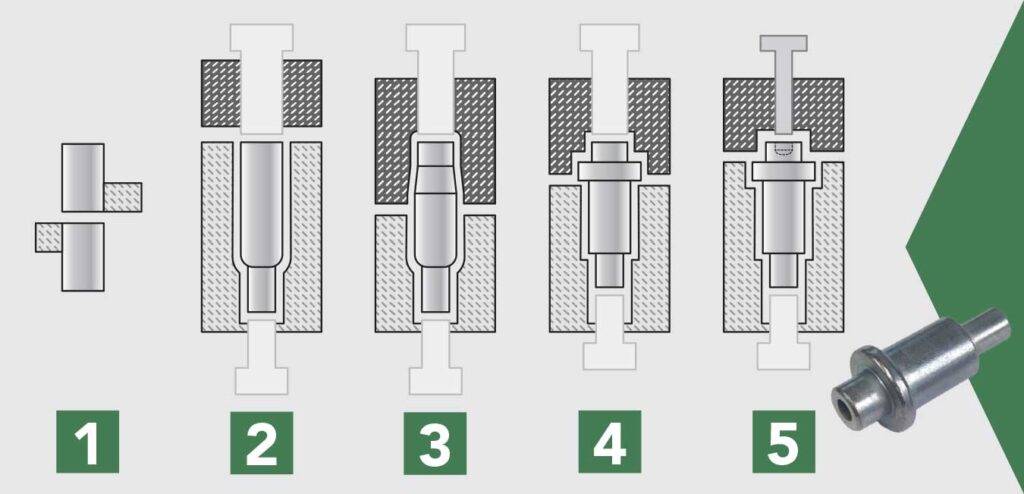
How Cold Heading Works: From Wire to Part
Cold heading is a high-speed, room-temperature metal-forming process. It reshapes wire or slugs into complex shapes using a series of engineered dies and punches. This process happens without external heat. Instead, it relies on the metal’s natural ductility and immense mechanical force.
The journey from raw material to a finished component typically follows these steps:
Starting with the Raw Material
The process begins with coiled metal wire. This wire often gets pre-treated for better formability. It then feeds directly into the cold heading machine.
The Forming Process: Step by Step
- Cut-off: A precise mechanism cuts the wire into individual blanks or slugs. These become your future parts.
- Feeding & Transfer: An automated system accurately feeds and transfers these blanks into various forming stations.
- Progressive Forming (The “Blows”): This is where shaping occurs. Blanks receive multiple high-force impacts from punches and dies. This progressively forms the metal. Two main techniques are involved:
- Upsetting: This compresses a blank section to increase its diameter. For example, it forms a screw head, collar, or flange on a shaft.
- Extrusion: This forces metal to flow through an opening, changing its cross-sectional area.
- Forward Extrusion: The metal pushes in the same direction as the punch. This reduces its diameter and increases its length, like forming shanks.
- Backward (Reverse) Extrusion: The metal flows backward around the punch. This creates internal cavities or holes. Examples include a socket recess in a screw or tubular rivets.
- Ejection: After the final forming blow, the precisely shaped part ejects from the machine. It is often ready for secondary operations like thread rolling or heat treatment.
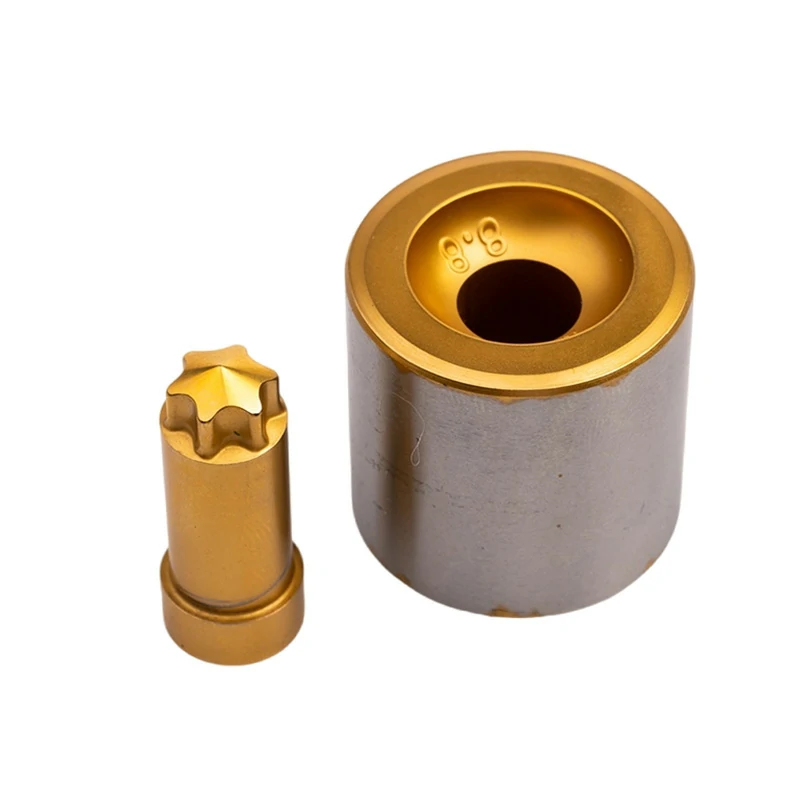
The tooling—the dies and punches—is crucial. Made from high-strength tool steel or carbide, these components must withstand tremendous forces. They also precisely guide metal flow to achieve intricate shapes and tight tolerances.
Why Choose Cold Heading? Key Advantages

Selecting cold heading for component manufacturing offers compelling benefits. These directly impact efficiency, cost, and product performance:
Maximized Material Efficiency
- Near Net-Shape Production: Cold heading forms parts to their final or near-final shape. It does so without cutting or removing material. This drastically reduces scrap, leading to exceptional material use.
- Reduced Waste: Machining generates up to 70% material waste as chips. In contrast, cold heading typically results in less than 5% waste. This directly translates into substantial material cost savings, especially in high-volume production.
Enhanced Strength and Durability
- Work Hardening: The cold deformation in cold heading “work hardens” the metal. This refines and aligns the material’s internal grain structure. It significantly increases tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance.
- Improved Grain Flow: Machined parts have cut grain lines. Cold-headed components, however, maintain continuous grain flow. This enhances the part’s overall durability and reliability under stress.
High-Volume, High-Speed Production
- Rapid Manufacturing: Cold heading machines are incredibly fast. They can produce hundreds of parts per minute. This high-speed capability is ideal for mass production.
- Consistency: The process ensures remarkable repeatability and consistency. This is crucial for maintaining quality in large batches.
Superior Precision and Finish
- Tight Tolerances: Cold heading can achieve very tight dimensional tolerances. These are often within +/- .002 inches or even finer. This precision is vital for components requiring exact fits.
- Excellent Surface Quality: Cold working often gives parts a smooth, dense, and aesthetically pleasing surface finish. This frequently eliminates the need for costly secondary finishing operations like grinding or polishing.
Simplified Assemblies with Part Consolidation
Complex designs can sometimes be cold headed as a single, stronger, and more cost-effective component. This reduces assembly time and costs for multi-piece assemblies. An example is a screw with an integrated washer.
Diverse Applications of Cold Heading
Cold heading’s versatility and benefits make it an indispensable process across numerous industries:
- Fasteners: This is its primary and most recognizable application. It includes screws, bolts, rivets, nuts, and specialty fasteners. These hold together virtually every modern product and structure.
- Automotive Industry: Examples include engine components, transmission parts, suspension elements, and interior fasteners.
- Aerospace & Defense: This sector uses high-strength, lightweight, and incredibly precise fasteners and structural components.
- Medical Devices: Miniature, highly precise, and often biocompatible fasteners and components for surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
- Electronics & Telecommunications: This includes small, intricate, and often non-magnetic parts like connectors, terminals, and pins.
- Construction & Infrastructure: Large anchor bolts, structural fasteners, and specialty components for buildings and bridges.
- Consumer Goods: Various intricate and reliable components found in appliances, furniture, and personal electronics.
Cold Heading in Context: How It Compares
Understanding cold heading’s unique advantages often involves comparing it to alternative manufacturing techniques:
- Cold Heading vs. Machining: The fundamental difference is metal forming versus metal removing. Machining cuts material, leading to significant scrap and potentially interrupting grain flow. Cold heading, however, forms the metal, preserving material and enhancing strength. It’s also typically far faster for high-volume production.
- Cold Heading vs. Hot Forging: Both are forming processes. However, cold heading occurs at room temperature, while hot forging involves heating the metal to high temperatures.
- Cold Heading: Offers tighter tolerances, superior surface finish, enhanced work-hardened strength, and is typically for smaller to medium-sized parts. It causes no scale formation from oxidation.
- Hot Forging: Provides greater ductility for very large or highly complex shapes. However, it yields less precise tolerances, can lead to oxidation and scaling, and generally doesn’t offer the same work hardening level.
- (Warm Heading): This is a hybrid process. It heats the material to an intermediate temperature. It balances the ductility of hot forging with the precision of cold heading. It is often used for forming tougher alloys.
Considerations and The Future of Cold Heading
While powerful, cold heading has some considerations. It is best suited for ductile metals. Also, the initial investment in robust, high-strength tooling can be significant. The cold working process can introduce residual stresses. However, proper design and post-processing (like stress relieving) can manage these.
Looking ahead, continuous innovation will enhance cold heading. This includes advancements in machinery, tooling materials, and metallurgy. As industries demand more efficient, sustainable, and high-performance manufacturing solutions, cold heading will remain a crucial process.
Partnering for Precision: Choose Xiluo Mold
At Xiluo Mold, we lead in advanced manufacturing. We have over 24 years of experience specializing in high-precision fastener molds and cold forming dies. We are proud to be the only one-stop R&D and production screw mold factory in China. Our commitment to quality is unwavering. We carefully source high-quality imported steel and implement strict quality control at every production stage. When you choose Xiluo Mold, you partner with an expert. We dedicate ourselves to delivering the precision, durability, and efficiency that defines the best in cold heading technology.




